Embark on a journey through the world of diabetes treatment options, where personalized plans and innovative technologies pave the way to a healthier life. Get ready to explore medications, lifestyle changes, monitoring practices, and much more in this engaging discussion.
Overview of Diabetes Treatment Options
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires proper management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. There are various treatment options available for individuals with diabetes, and personalized treatment plans are crucial to address each person’s specific needs and goals.
Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans take into account factors such as age, lifestyle, overall health, and preferences of the individual. By tailoring the treatment approach to each person, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes and ensure that the management of diabetes is effective and sustainable.
Goals of Diabetes Treatment
The primary goals of diabetes treatment include managing blood glucose levels, preventing complications, and improving overall health and well-being. Different treatment options aim to achieve these goals through various mechanisms such as insulin therapy, oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly.
Medication Options for Diabetes

Diabetes management often involves the use of medications to help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Common medications used in the treatment of diabetes include insulin, metformin, and sulfonylureas.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose for energy. It is commonly used in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin. There are different types of insulin, such as rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. Insulin is usually injected subcutaneously, and the dosage may vary depending on factors like diet, exercise, and blood sugar levels.
Metformin
Metformin is a medication that helps lower blood sugar levels by reducing glucose production in the liver and increasing insulin sensitivity in the body. It is often prescribed for type 2 diabetes and is usually taken orally. Metformin is known for its effectiveness, low risk of hypoglycemia, and potential benefits beyond blood sugar control, such as weight loss and cardiovascular protection.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas are a class of medications that work by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin. This helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production. Some common sulfonylureas include glyburide, glipizide, and glimepiride. While these medications can be effective in managing diabetes, they may also carry a risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain.Medication adherence plays a crucial role in managing diabetes effectively.
It is important for individuals to take their medications as prescribed by their healthcare provider to ensure optimal blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications. Missing doses or not following the recommended dosage instructions can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and may impact overall health outcomes. Regular communication with healthcare providers and pharmacists can help address any concerns or challenges related to medication adherence.
Lifestyle Changes and Diabetes Management
To effectively manage diabetes, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels. By focusing on diet and exercise, individuals with diabetes can better regulate their glucose levels and improve overall health.
Dietary Modifications for Glucose Regulation
- Limiting sugar and refined carbohydrates: Consuming foods high in sugar and refined carbs can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Opt for whole grains, fruits, and vegetables instead.
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake: Keeping track of carbohydrate consumption can help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Including lean proteins and healthy fats: Protein and fats can help slow down the absorption of sugar in the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes.
- Eating smaller, frequent meals: Spreading out meals throughout the day can help prevent drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Importance of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for diabetes management and overall health. Exercise helps increase insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better utilize glucose for energy. It also aids in weight management and reduces the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Exercise is not only beneficial for blood sugar control but also contributes to improved cardiovascular health and mood.
Engaging in activities like walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes a day can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
Monitoring and Self-Care Practices
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective diabetes management. By keeping track of your levels, you can make informed decisions about your diet, medication, and lifestyle choices to keep your diabetes in check.Self-care practices play a vital role in preventing complications associated with diabetes. This includes proper foot care to prevent infections and injuries, as well as regular eye examinations to detect any early signs of diabetic retinopathy.
Tips for Effective Diabetes Management
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Follow a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay physically active with regular exercise to help control blood sugar levels.
- Take your medications as prescribed and never skip doses.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of complications.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in Diabetes Treatment
Emerging technologies and innovations in diabetes treatment have revolutionized the way patients manage their condition. From continuous glucose monitoring devices to artificial pancreas systems, these advancements have the potential to greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
Continuous glucose monitoring devices are wearable sensors that track glucose levels throughout the day, providing real-time data to patients and healthcare providers. These devices eliminate the need for frequent finger pricks and allow for better management of blood sugar levels. The data collected can also help identify trends and patterns, leading to more personalized treatment plans.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Artificial pancreas systems combine continuous glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery, creating a closed-loop system that mimics the function of a healthy pancreas. These systems can adjust insulin dosages in real time based on glucose levels, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. By automating this process, patients can achieve better blood sugar control with less effort.
Ongoing Research and Developments
Researchers are continuously exploring new technologies and innovations in diabetes treatment. From advanced insulin delivery systems to implantable devices that release insulin as needed, the future looks promising for individuals living with diabetes. By staying updated on the latest developments in the field, healthcare providers can offer their patients the most effective and cutting-edge treatment options available.
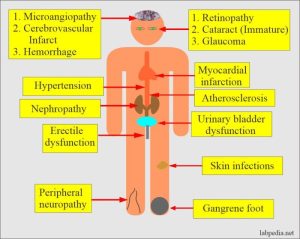
Relationship between Diabetes and Other Health Conditions
Diabetes is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on various aspects of a person’s health. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and other health conditions is crucial for effective management and overall well-being.
Diabetes and Heart Disease
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease compared to those without diabetes. The presence of diabetes can contribute to the development of cardiovascular issues such as heart attacks, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Managing both diabetes and heart disease simultaneously is essential for reducing the risk of complications. This may involve lifestyle changes, medication management, and regular monitoring to control blood sugar levels and maintain heart health.
Diabetes and Foot Health
Diabetes can have a negative impact on foot health, increasing the risk of complications such as neuropathy, foot ulcers, and infections. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prioritize foot care, including regular examinations by a healthcare provider.
Proper foot care, including daily inspections, appropriate footwear, and prompt treatment of any issues, can help prevent serious complications and maintain overall foot health in individuals with diabetes.
Diabetes and Eating Disorders
There is a complex relationship between diabetes and eating disorders, as managing both conditions effectively can be challenging. Individuals with diabetes may be at a higher risk of developing eating disorders, which can impact their ability to manage blood sugar levels and overall health.
Addressing the psychological and emotional aspects of diabetes and eating disorders, along with proper education, support, and treatment, is important for promoting a healthy relationship with food and managing diabetes effectively.
Final Summary
As we wrap up our exploration of diabetes treatment options, remember that managing diabetes is not just about medications but also about lifestyle changes and continuous monitoring. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take charge of your health!
FAQ Summary
Can diabetes be managed solely through medication?
No, a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management.
Are there any new technologies that are revolutionizing diabetes treatment?
Yes, advancements like continuous glucose monitoring devices and artificial pancreas systems are making a significant impact on diabetes management.
How important is regular physical activity in diabetes management?
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels and overall health for individuals with diabetes.