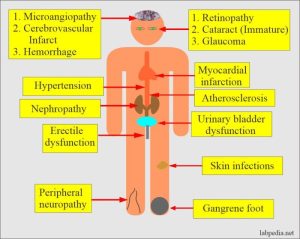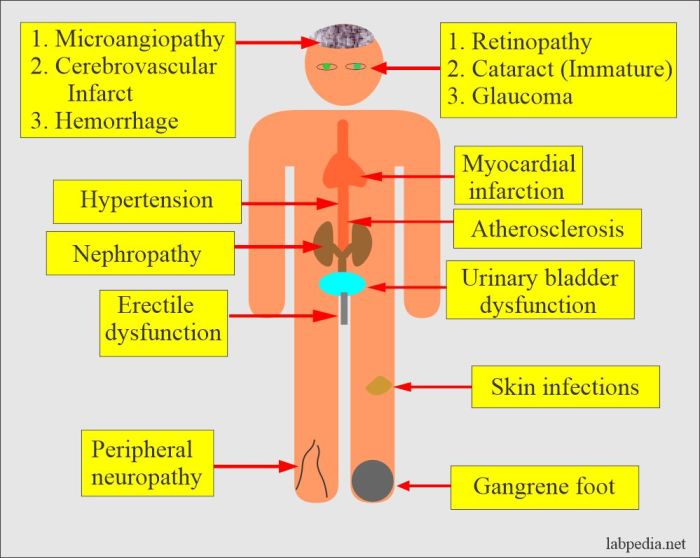
Get ready to dive into the world of diabetes complications prevention! From cosmetic surgery to foot health, heart disease, overall health, and eating disorders, we’ve got you covered with essential information and tips to keep you in top shape. Let’s explore how to stay healthy and happy while managing diabetes complications.
Cosmetic Surgery
Cosmetic surgery can have a significant impact on individuals with diabetes, as it presents unique challenges and risks that need to be carefully considered before undergoing any procedures. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to consult their healthcare professionals to discuss the potential risks and benefits of cosmetic surgery.
Examples of Cosmetic Procedures
- Rhinoplasty: A nose job to improve the shape and function of the nose.
- Liposuction: A procedure to remove excess fat from specific areas of the body.
- Breast augmentation: Enhancing the size and shape of the breasts through implants.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before undergoing any cosmetic surgery, individuals with diabetes should consult their healthcare professionals to assess their overall health and ensure they are in optimal condition for the procedure. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on managing blood sugar levels, preventing infections, and minimizing the risk of complications during and after surgery.
Foot Health
Diabetes can lead to a variety of foot health issues due to nerve damage and poor blood circulation. Common problems include neuropathy, calluses, foot ulcers, and infections.
Tips for Maintaining Good Foot Health
- Avoid walking barefoot to prevent injuries and infections.
- Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or redness.
- Keep your feet clean and dry to prevent fungal infections.
- Trim your toenails carefully to avoid ingrown nails.
- Avoid using heating pads or hot water bottles on your feet.
The Role of Proper Footwear
Wearing the right footwear is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent foot complications. Proper shoes should provide support, cushioning, and protection. Look for shoes with a wide toe box, good arch support, and a soft lining to reduce pressure on the feet. It’s also essential to ensure that your shoes fit well and do not rub or cause friction that could lead to sores or blisters.
Heart Disease
Diabetes and heart disease are closely linked, as individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease compared to those without diabetes. High blood glucose levels over time can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart.
Preventive Measures for Reducing Risk of Heart Disease
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Control blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of heart complications.
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels regularly.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or counseling.
Importance of Regular Check-ups and Screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings are essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor their heart health and detect any potential issues early. These screenings may include blood tests for cholesterol levels, blood pressure measurements, and evaluations of heart function. Early detection and intervention can help prevent or manage heart disease effectively in individuals with diabetes.
Health Diabetes
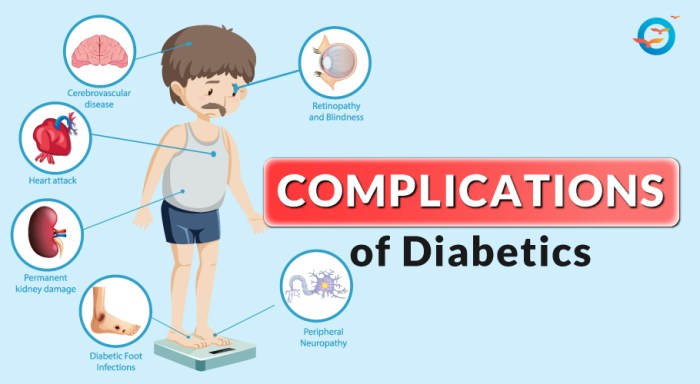
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires diligent management to prevent complications. Maintaining overall health is crucial in controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes-related issues.
Significance of Overall Health
- Regular exercise plays a vital role in managing diabetes as it helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- A balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help regulate blood sugar and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Weight management is essential for individuals with diabetes as excess weight can worsen insulin resistance and increase the likelihood of complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of diabetic neuropathy and other complications.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and following a consistent meal plan can aid in diabetes management and prevent sudden spikes or drops in glucose levels.
- Getting regular check-ups and screenings to detect any early signs of complications such as eye problems, kidney issues, or nerve damage.
Role of Medication Adherence
- Consistent adherence to prescribed medications, including insulin or oral medications, is crucial in maintaining stable blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
- Following the healthcare provider’s recommendations for medication dosage and timing can help individuals with diabetes effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
- Consulting with healthcare professionals regularly and adjusting medication regimens as needed based on blood sugar levels and overall health status.
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders can have a significant impact on individuals with diabetes, as they can disrupt blood sugar levels and interfere with proper management of the condition. Disorders like anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and binge eating can lead to irregular eating patterns, skipping meals, or consuming excessive amounts of food in a short period of time.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications. It involves consuming a variety of nutrients from different food groups in appropriate portions. Ensuring a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals can help regulate blood glucose levels and support overall health.
- Aim to include a mix of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables in your meals.
- Avoid overly processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat snacks that can spike blood sugar levels.
- Consult with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that meets your nutritional needs while managing diabetes.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and adjust your diet as needed based on your readings.
Promoting a Healthy Relationship with Food
Maintaining a healthy relationship with food is essential for individuals with diabetes to prevent the development or exacerbation of eating disorders. Here are some tips to foster a positive mindset towards eating while managing diabetes:
- Avoid labeling foods as “good” or “bad” and instead focus on moderation and balance in your diet.
- Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger cues, savoring each bite, and eating slowly to prevent overeating.
- Engage in regular physical activity to support a healthy metabolism and overall well-being.
- Seek support from healthcare professionals, therapists, or support groups if you’re struggling with disordered eating behaviors.
End of Discussion

As we wrap up our journey through diabetes complications prevention, remember that taking care of your health is a priority. By following the advice and tips shared here, you can lead a fulfilling and healthy life despite the challenges of diabetes. Stay informed, stay proactive, and stay healthy!
Query Resolution
How can cosmetic surgery impact individuals with diabetes?
Cosmetic surgery procedures may have specific risks for individuals with diabetes, such as delayed wound healing or infection. It’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider before considering any cosmetic procedures.
What are some preventive measures to reduce the risk of heart disease in individuals with diabetes?
Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and regular check-ups are key in reducing the risk of heart disease for individuals with diabetes.
How can eating disorders affect individuals with diabetes?
Eating disorders can disrupt blood sugar levels and lead to serious complications for individuals with diabetes. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet and seek support if struggling with disordered eating habits.